What Is The Low FODMAP Diet + What You Need To Know
Hi everyone. Welcome back to our channel.
What is the Low FODMAP Diet?
What are FODMAPs and how do they impact our digestive health?
What's the connection between a low FODMAP diet and IBS?
How do you get started on a low FODMAP diet?
What are some examples of some low FODMAP foods and what are some examples of some high FODMAP foods that you should avoid?
These are the questions we'll be diving into in today's video.
I'm Katie Bailey. I'm a gut health dietician at Oswald Digestive Clinic, where we help individuals improve and resolve their bothersome gut issues. If you're interested in learning more about gut health, I'll link off free guide 5 Ways to Improve Your Gut Health HERE.
All right, let's get started on today's topic.
[Video Transcript Below Video - it is the same information as in the video]
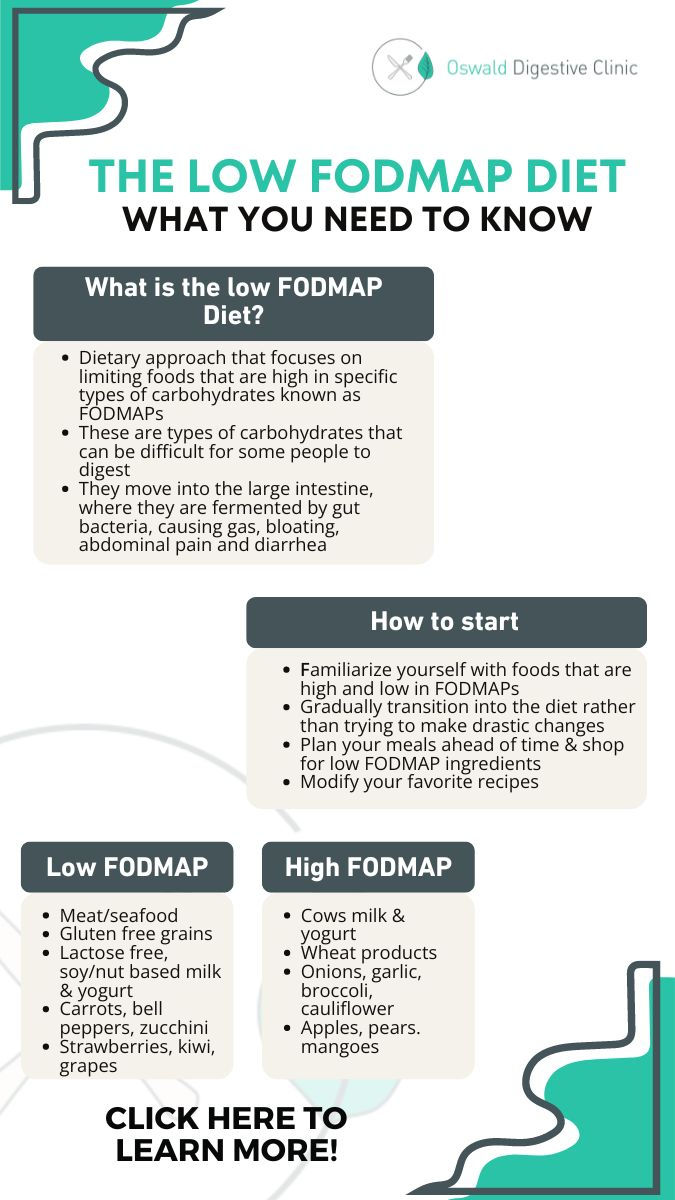
What is the low FODMAP diet?
The low FODMAP diet is a dietary approach that focuses on limiting foods that are high in specific types of carbohydrates known as FODMAPs.
The goal of this diet is to reduce high FODMAP foods and replace them with low FODMAP foods in an effort to provide symptom relief.
Ideally, once your symptoms are resolved, then you can start reintroducing foods back in.
The first phase of this diet is called the elimination phase, which typically lasts between two and six weeks. During this phase, you want to remove all high FODMAP foods from your diet while monitoring your symptoms.
It's important to be strict during this phase because you want to really make sure if your symptoms are improving or not. After completing the elimination phase, you move on to the reintroduction phase.
During this phase, you want to reincorporate specific high FODMAP foods back into your diet one at a time, and to determine what your tolerance level is for that specific food.
When reintroducing foods, it's a good idea to start with small portions and increase gradually, and it's also good to start with just one FODMAP food group and then monitor your symptom over a few days before moving on to the next group.
And it's important to remember that no two people are alike, so this diet may need to be tweaked to meet your individual needs.
What are FODMAPs and how do they impact our digestive health?
FODMAP is an acronym that stands for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols.
These are types of carbohydrates that some individuals have a hard time digesting, so when these carbohydrates are not properly absorbed in the small intestines, they move down to the large intestines where they are fermented by our gut bacteria leading to uncomfortable symptoms like gas, bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Severity of these symptoms is going to vary from person to person, and some individuals may be more sensitive to certain types of FODMAPs than others.
So what is the connection between a low FODMAP diet and IBS?
For those of you who are not familiar with IBS, IBS is also known as irritable bowel syndrome, and it is a GI condition that's characterized by abdominal pain and alter bowel movements.
Research has shown that following a low FODMAP diet can reduce IBS symptoms in up to 70% of individuals with this condition.
So by limiting the intake of high FODMAP foods, this can reduce the fermentation process in the gut and potentially alleviate symptoms associated with IBS.
However, it's important to note that low FODMAP diet is not a cure for IBS, but rather a management strategy to help control your symptoms. This diet may also be beneficial for other GI conditions like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, also known as sibo.
How do you get started with the low FODMAP diet?
So transitioning to a low FODMAP diet can be a significant lifestyle change and can be overwhelming for some people.
Here are some tips to help get you started.
The first thing you want to do is you want to familiarize yourself with the foods that are high and low.
In FODMAPs, there are many different resources. You can use books and guides and some applications as well that can help you identify these.
The one I like a lot is the Monash University app because you can go on and search for particular foods and it will tell you whether it's low, moderate, or high in FODMAPs.
Second, you want to gradually transition into a low FODMAP diet rather than making drastic changes all at once because that can be quite overwhelming and you're more likely to stick to the diet if you do it gradually.
Also, you want to plan your meals ahead of time, so by carving out time every week to plan your meals, this is going to ensure that you have the ingredients that you need to create your low FODMAP recipes.
Shop for low FODMAP ingredients, learn which foods are considered low fodmap, and make sure you have plenty of those foods on hand to use in your recipes. Keep low FODMAP snacks on hand as well.
Things like rice cakes and carrots and hard boiled eggs. That way you always have a snack available that's going to fit into the diet.
Modify your favorite recipes. Choose take the high FODMAP foods out of your recipes and replace them with low FODMAP food options. And then lastly, adjust your portion sizes.
Sometimes you can still have a high FODMAP food in a low, smaller portion size.
What are some examples of some low FODMAP food options?
When it comes to protein, all your meat, poultry, and seafood are going to be considered low FODMAP unless prepared with other high FODMAP foods.
When it comes to dairy, you want to choose lactose free soy or nut-based milks and yogurts for produce, things like carrots and bell peppers, zucchini strawberries, kiwi, and grapes are all good options for low fodmap.
And then you want to also choose gluten-free grains, quinoa, rice, and oats.
What are some examples of some high FODMAP foods to avoid?
Well, you want to avoid regular cow's, milk and yogurt.
You also want to look at avoiding all wheat products, and then when it comes to produce things like onions and garlic, broccoli, cauliflower and mushrooms, apples, pears, and mango would all be foods that you should avoid.
Now, obviously this is not an extensive list of all the different foods, but I just wanted to give you an example of some things in each category.
Now, like I mentioned before, Monash University is a great resource, both their website and their app, and can be very beneficial in helping you determine which foods fit into which category.
Before we wrap up our topic for today, I wanted to mention that the low FODMAP diet is not intended for long-term use.
It's a short-term intervention that can help you identify food triggers and help manage your digestive symptoms. The diet is typically followed for six to eight weeks after which then high FODMAP foods are then reintroduced to determine an individual's tolerance of that food.
It's important to remember that we are all unique and there are other possible causes for our digestive issues, things like stress and lack of sleep and other medical conditions.
So I highly recommend that you work with a professional that can help you with not only the diet, but also to determine if there's any other possible causes for your symptoms.
So that's it for today's video. If you liked this video, please hit the like button and subscribe for more nutrition videos.
If you're interested in working with our clinic, you could click HERE to make an appointment.
We do take insurance and you can find more information about that on our website.
Thank you for watching.
I'll see you next time.
Bye.
If you'd like to explore any of this information further or obtain an individualized nutrition plan, you can schedule an initial appointment at our clinic. We also take insurance and some of our clients get full coverage, which is great.
Curious about what type of gut you have? Take our Free Quiz now!











